Openflow y SDN (página 2)
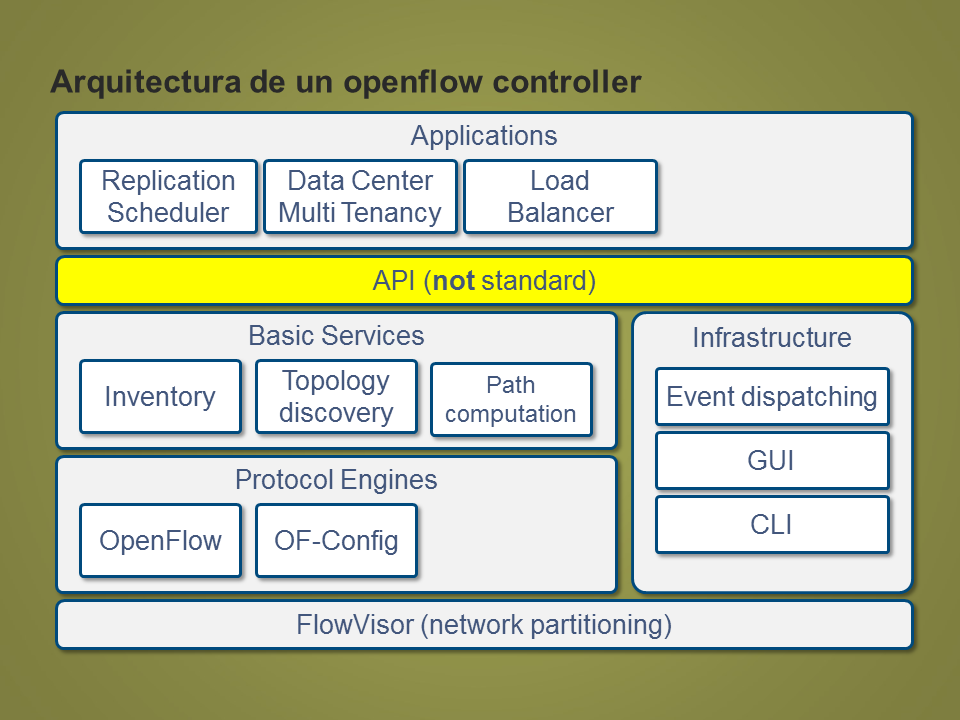
Arquitectura de un openflow controller
Protocol Engines
OpenFlow
OF-Config
Basic Services
API (not standard)
Topology
discovery
Path
computation
Inventory
Infrastructure
Event dispatching
GUI
CLI
FlowVisor (network partitioning)
Applications
Replication
Scheduler
Data Center
Multi Tenancy
Load
Balancer
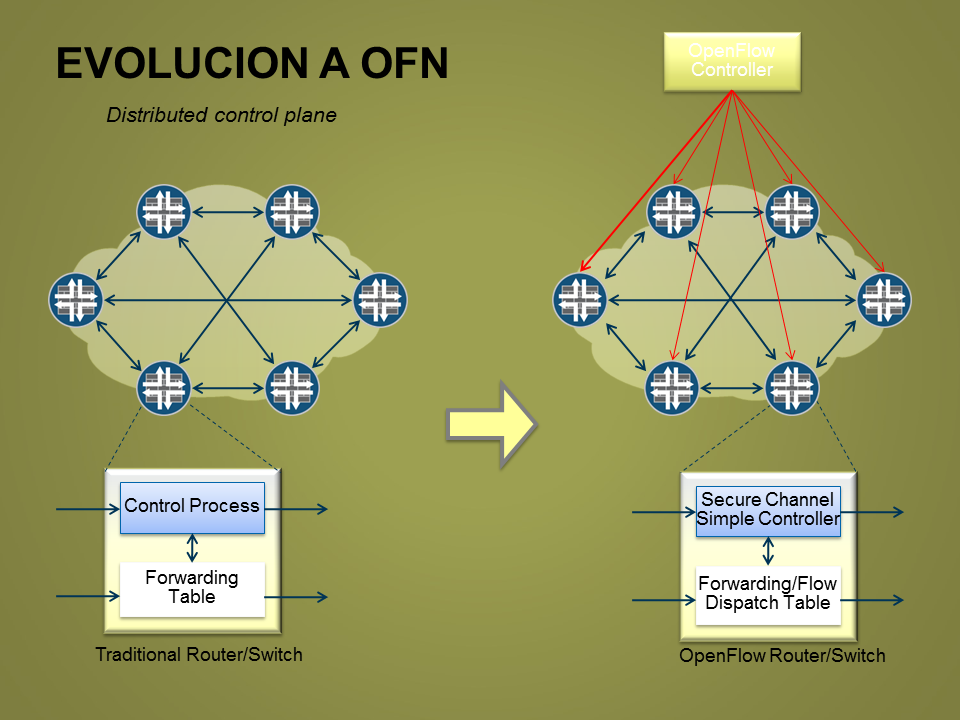
OpenFlow
Controller
Traditional Router/Switch
OpenFlow Router/Switch
Control Process
Forwarding Table
Secure Channel
Simple Controller
Forwarding/Flow Dispatch Table
Distributed control plane
EVOLUCION A OFN

Controller
PC
Hardware
Layer
Software
Layer
Flow Table
(Gp:) MAC
src
(Gp:) MAC
dst
(Gp:) IP
Src
(Gp:) IP
Dst
(Gp:) TCP
sport
(Gp:) TCP
dport
(Gp:) Action
OpenFlow Client
(Gp:) *
(Gp:) *
(Gp:) 5.6.7.8
(Gp:) *
(Gp:) *
(Gp:) *
(Gp:) port 1
port 4
port 3
port 2
port 1
1.2.3.4
5.6.7.8
Ejemplo de OpenFlow
13

TIPOS DE MENSAJES
Tres tipos de mensajes y cada mensaje con múltiples subtipos.:, controller-to-switch, asynchronous y symmetric.
Controller-to-switch messages are initiated by the controller and used to directly manage or inspect the state of the switch.
Features (query capabilities), modify-state(add/delete/modify flow/group entry), read-state, packet-out
Asynchronous messages are initiated by the switch and used to update the controller of network events and changes to the switch state.
Such as ?ow-removed, packet-in, port-status
Symmetric messages are initiated by either the switch or the controller and sent without solicitation.
hello, echo (request/reply), experimenter

OpenFlow Basics Flow Table Entries (1.0)
Switch
Port
MAC
src
MAC
dst
Eth
type
VLAN
ID
IP
Src
IP
Dst
IP
Prot
L4
sport
L4
dport
Rule
Action
Stats
Forward packet to zero or more ports
Encapsulate and forward to controller
Send to normal processing pipeline
Modify Fields
Any extensions you add!
+ mask what fields to match
Packet + byte counters
15
VLAN
pcp
IP
ToS

Examples (1/2)
Switching
*
(Gp:) Switch
Port
(Gp:) MAC
src
(Gp:) MAC
dst
(Gp:) Eth
type
(Gp:) VLAN
ID
(Gp:) IP
Src
(Gp:) IP
Dst
(Gp:) IP
Prot
(Gp:) TCP
sport
(Gp:) TCP
dport
(Gp:) Action
*
00:1f:..
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
port6
Flow Switching
port3
(Gp:) Switch
Port
(Gp:) MAC
src
(Gp:) MAC
dst
(Gp:) Eth
type
(Gp:) VLAN
ID
(Gp:) IP
Src
(Gp:) IP
Dst
(Gp:) IP
Prot
(Gp:) TCP
sport
(Gp:) TCP
dport
(Gp:) Action
00:20..
00:1f..
0800
vlan1
1.2.3.4
5.6.7.8
4
17264
80
port6
Firewall
*
(Gp:) Switch
Port
(Gp:) MAC
src
(Gp:) MAC
dst
(Gp:) Eth
type
(Gp:) VLAN
ID
(Gp:) IP
Src
(Gp:) IP
Dst
(Gp:) IP
Prot
(Gp:) TCP
sport
(Gp:) TCP
dport
(Gp:) Action
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
22
drop
16

Examples (2/2)
Routing
*
(Gp:) Switch
Port
(Gp:) MAC
src
(Gp:) MAC
dst
(Gp:) Eth
type
(Gp:) VLAN
ID
(Gp:) IP
Src
(Gp:) IP
Dst
(Gp:) IP
Prot
(Gp:) TCP
sport
(Gp:) TCP
dport
(Gp:) Action
*
*
*
*
*
5.6.7.8
*
*
*
port6
VLAN Switching
*
(Gp:) Switch
Port
(Gp:) MAC
src
(Gp:) MAC
dst
(Gp:) Eth
type
(Gp:) VLAN
ID
(Gp:) IP
Src
(Gp:) IP
Dst
(Gp:) IP
Prot
(Gp:) TCP
sport
(Gp:) TCP
dport
(Gp:) Action
*
*
vlan1
*
*
*
*
*
port6,
port7,
port9
00:1f..
17

Secure Channel
Flow Table
OpenFlow Controller
OpenFlow Protocol
SSL/TLS
OpenFlow v1.0 Switch
sw
hw
OpenFlow v1.0 Switch

Secure Channel
Flow Table
OpenFlow Controller
OpenFlow Protocol
SSL/TLS
OpenFlow v1.1 Switch
Flow Table
…
Pipeline
Group Table
OpenFlow v1.1 Switch

Secure Channel
Flow Table
OpenFlow Controller
OpenFlow Protocol
SSL/TLS
OpenFlow v1.1 Switch
Flow Table
…
Pipeline
Group
Table Table
OpenFlow v1.1 Switch

CASOS PRACTICOS

Data center interconnect wanOpenflow instead of routing protocols
OpenFlow switch
no routing protocols
Logically centralized
OpenFlow controller

Data center con Arquitectura de SDN
Physical
IP Fabric
Virtualized
Network
Virtualized
Compute
Virtualized
storage
Virtualized
services
Centralized
Orchestration

Multi-tenancy using overlay networks
Hypervisor
Virtual switch
Virtual machine
Overlay tunnel

Virtualized services
Virtual firewall service

centralized orchestrationOF compute, storage, and network
Centralized
Orchestration
Compute
Storage
Network
The IP fabric
was not touched
OpenFlow

Juniper is the recognized leader of the network programmability movement, which is the conceptual foundation underlying the SDN approach.
Long before the term “SDN” was coined, our disruptive network architectures were built on the premise of using innovative software to give customers unprecedented levels of flexibility and control, with an end goal of transforming the economics and experience of networking.
By simultaneously simplifying and opening up the network, Juniper pioneered the core capabilities and concepts behind SDNs.
Posicionamiento de SDN
 Página anterior Página anterior |   Volver al principio del trabajo Volver al principio del trabajo | Página siguiente  |