This presentation draws on ideas from
Professor Porter"s books and articles, in particular,
Competitive Strategy (The Free Press, 1980);
Competitive Advantage (The Free Press, 1985); "What is
Strategy?" (Harvard Business Review, Nov/Dec 1996); and
On Competition (Harvard Business Review, 2008). No part
of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval
system, or transmitted in any form or by any
means—electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or
otherwise—without the permission of Michael E. Porter.
Additional information
may be found at the website of the
Institute for Strategy and Competitiveness, www.isc.hbs.edu.
2. The Role of Business in
Society
• Only business can create
prosperity
• Healthy businesses need a healthy
community BUT
• There is a growing awareness
of major societal challenges
• Companies are increasingly perceived
to be prospering at the expense of the broader
community
• Business increasingly is seen as
a major cause of social, environmental, and
economic problems
• Government and civil society often
attempt to address societal issues at the expense of
business
?
• Despite growing corporate
citizenship activities, the legitimacy of
business has fallen
3. The Role of a Company in Its
Communities (3,4,5)

Philanthropy ? Corporate Social
Responsibility (CSR) ? Creating Shared Value (CSV)
Philanthropy
• Donations to worthy social
causes
Corporate Social
Responsibility
• Good corporate citizenship and
compliance with community nstandards
• Sustainability
Creating Shared Value
• Integrating societal improvement
into economic value creation itself
6. The Concept of Shared Value
(6,7)
Shared Value: Corporate policies and
practices that enhance competitiveness of the company while
simultaneously advancing social and economic conditions in the
communities in which it operates
• Create economic value by
creating societal value
What is good for the community is good
for business
• All profit is not equal.
Profit involving shared value enables society to advance and
companies to grow faster
?
• Concern with societal issues
will be a defining characteristic of the post-crisis
era
• Incorporating societal issues into
strategy and operations is the next major transformation
in management thinking
• Shared value represents the next
evolution of capitalism
8. Moving to Shared Value

CSR
• Values: "doing good," good
citizenship,
philanthropy, and sustainability
• Discretionary
• Separate from profit
maximization
• Agenda externally
determined
• Impact is limited by the
corporate footprint and CSR budget
Example: Fair trade purchasing
CSV
• Value: economic and societal
benefits relative to cost
• Integral to
competing
• Essential to profit
maximization
• Agenda is business
specific
• Mobilizes the entire company
budget
Example: Transforming procurement to
increase quality and yield
* In both cases, compliance with
laws and ethical standards and reducing harm for corporate
activities are assumed
9. Business and Society: Why the
Disconnect?

Company Profitability and Growth ?
Social and
Economic Development
• Companies adopted a narrow
model of economic value creation
? Meeting conventional needs of
conventional customers
? Driving revenue through
acquisitions instead of new business creation
? Profit improvement through downsizing,
outsourcing, relocating, and globalizing
? Emphasis on capital structure
instead of real value creation
? Societal issues treated as outside
the scope of business
?
• Huge societal needs go
unmet
• Growth and innovation
suffer
10. Societal Needs and Economic Value
Creation

Company Productivity
Environment impact
Supplier access and
viabilityEmployee skills
Gender and racial
equityWorker safety
Employee health
Water use
Energy use
• Social deficits create
economic cost
• External conditions shape
internal company productivity
• Social needs represent the
largest market opportunities
• There is a growing congruence
between economic value creation and societal
objectives
11. Levels of Shared
Value
• Reconceiving customer needs,
products, and markets
• Redefining productivity in
the value chain
– How the organization conducts its
business
• Enabling local cluster
development
12. Reconceiving Products and
Markets
• Design products and services to
address societal needs
– E.g., environmental impact, safety,
health, education, nutrition, living with disability, housing,
financial security
• Open new markets by serving
unmet needs in underserved communities
– Often requires redesigned products
or different distribution methods
• Businesses have the potential to be
more effective than governments and NGOs in creating and
marketing solutions to community problems
?
• New needs and new markets open up
opportunities to differentiate, innovate, and
grow
• A new generation of social
entrepreneurs is capturing these opportunities, often faster
than mainstream businesses
13. Creating Shared Value in
Products
Dow Chemical Insect
Control
The SpinetoramTM Family of insect control
products are derived from a biological organism that
provides control of a broad spectrum of insect pests in a variety
of crops
• Natural degradation through UV light
and soil microbes
• Low solubility in water
• Favorable toxological
profile
• Carries lowest human hazard
label
• Organic version available
?
• Ability to be applied at lower
rates than conventional insecticides
• Low impact on beneficial
insects
• Double-digit growth since
launch in 2010
14. Creating Shared Value in
Products
Intuit SnapTax
SnapTax provides low-income
consumers with access to tax preparation services over the phone
and enables rapid refunds
• 15 minutes for $15,
electronic filing included
• Data extracted from mobile phone
photos of W-2s via optical character recognition
• Debit card option for direct
deposit of refunds for unbanked households
• Simple IRA option to enable
use of refund for retirement savings
15. Creating Shared Value in Products
and Markets
Novo Nordisk in China
Diabetes training programs together
with governments, NGOs, and opinion leaders to promote the latest
thinking among physicians on diabetes prevention,
screening,
treatment, and patient
communication
• Targeting smaller cities
• 220,000 sessions to date
"Diabetes bus" program to raise
patient awareness and provide on-site advice, NovoCare telephone
hotline allows patients to reach specialists with questions.
NovoCare Club provides ongoing updates to members.
• Patient education focuses on
prevention, lifestyle changes, and effective use of insulin
products
?
• 280,000 patients educated to
date
• Since 1997, this program is
estimated to have reduced healthcare costs in China by
$700 million through reducing diabetes related
complications
• Novo Nordisk sales have
increased by an estimated $114 million
16. Discovering Product and Market
Opportunities to Create Shared Value
• Redefine the business around
unsolved customer problems or concerns, not traditional
product definitions
– Or the customer"s customer
• Think in terms of improving
lives, not just meeting consumer needs
• Identify customer groups that have
been poorly served or overlooked by the industry"s
products
• Start with no preconceived
constraints about product attributes, channel configuration,
or the economic model of the business
(e.g., small loans are
unprofitable)
17. Redefining Productivity in the Value
Chain

Margin
Firm Infrastructure – (e.g. Financing,
Planning, Investor Relations)
Procurement – (e.g. Components,
Machinery, Advertising, Services)
Technology Development – (e.g. Product
Design, Testing, Process Design, Material Research, Market
Research)
Human Resource Management – (e.g.
Recruiting, Training, Compensation System
?
Inbound Logistics – (e.g. Incoming
Material Storage, Data Collection, Service, Customer
Access)
Operations – (e.g. Assembly, Component
Fabrication, Branch Operations)
Outbound Logistics – (e.g. Order
Processing, Warehousing, Report Preparation)
Marketing & Sales – (e.g. Sales
Force, Promotion, Advertising, Proposal Writing,
Website)
After-Sales Service – (e.g.
Installation, Customer Support, Complaint Resolution,
Repair
• Purchasing
• Resource use
• Energy use
• Logistical efficiency
• Employee productivity
• Location of facilities and the
supply chain
18. Identifying Opportunities for Shared
Value in Mining
The Value Chain
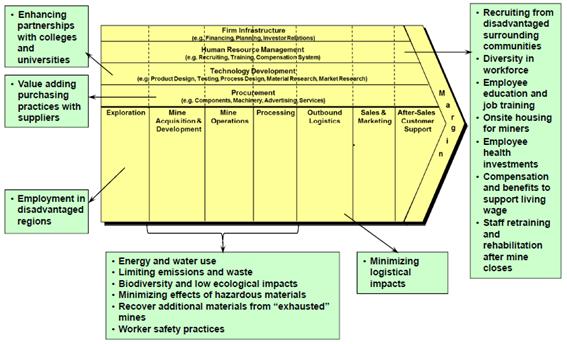
Margin
1. Firm Infrastructure – (e.g.
Financing, Planning, Investor Relations)
• Enhancing partnerships with
colleges and universities
2. Human Resource
Management
• Recruiting from disadvantaged
surrounding communities
• Diversity in
workforce
• Employee education and job
training
• Onsite housing for
miners
• Employee health
investments
• Compensation and benefits to
support living wage
• Staff retraining and
rehabilitation after mine closes
3. Technology
Development
• Enhancing partnerships with
colleges and universities
Procurement
• Value adding purchasing practices
with suppliers
Exploration
• Employment in
disadvantagedregions
Mine acquisition &
Development
Mine Operations
Processing
• Energy and water
use
• Limiting emissions and
waste
• Biodiversity and low ecological
impacts
• Minimizing effects of hazardous
materials
• Recover additional materials from
"exhausted" mines
• Worker safety
practices
Outbound Logistics
• Minimizing logistical
impacts
Sales & and marketing
After-Sales customer
Support
19. Cluster development in the
company"s
Major Locations
• A strong local cluster improves
company growth and productivity
– Local suppliers
– Supporting institutions and
infrastructure
– Related businesses
• Companies, working
collaboratively, can catalyze major improvements in
the local cluster and business
environment
• Local cluster development
strengthens the link between a company"s
success and community success
20. Local Cluster
Development
Cut Flowers in Kenya

21. Local Cluster
Development
Anglo-American
• Anglo American has established Anglo
Zimele, a South African enterprise investment fund, for
mining-related small and medium-sized businesses in South
Africa
• As of 2010, the fund had invested in
509 businesses, which collectively employed 9,514 people
with annual revenues of $215 million Community value
• 10,000 new jobs
created
• Significant increase in
income for SME employees and owners
• Spillover effects of these
new businesses on their communities Economic value
• Anglo-American has created reliable,
high-quality local suppliers
• Local suppliers reduce transaction
costs and improve service levels and
quality
22. Integrating Shared Value
Approaches
Nespresso
• Implementing shared value in
sourcing premium coffees from farmers in Costa Rica,
Guatemala, Colombia, and Ghana
• Upgrading the cluster
– Supporting local cluster
development in coffee growing regions, including
establishment of cluster institutions
– Partnering with
stakeholders
Shared Value
Farmers
• Better yields
• Better prices
• Better processing
Community
• Environmental
sustainability
• Economic development
Nespresso
• Stable supply
• Better quality
• Reinforces strategic
positioning
23. Creating Shared Value: Deciding
Where to Concentrate
Nestlé

–Nutrition
– Water
– Rural Development
?
• Opportunities to create shared value
are inevitably tied closely to a company"s particular
businesses
24. Measuring Shared
Value
Economic Value
• Profitability
• Revenue
• ROI
• Industry growth
Societal Value
• Specific societal benefits
achieved
?
• Shared value measurement
links economic and social improvement metrics
25. Creating Shared Value
Implications for Government and Civil
Society
• Government and NGOs often assume
that trade-offs between economic and social benefits are
inevitable
?
• Government and NGOs will be most
effective if they enable shared value by
business
• NGOs bring unique expertise,
implementation capacity, and relationships of trust
with communities
A New Type of NGO
TechnoServe
RootCapital
– Promotes the development of agricultural
clusters in more than 30 countries
– Provides financing to more than 400,000
farmers and businesses
Bill & Melinda Gates
Foundation
– Forms partnerships with global
corporations to foster agricultural clusters
• Governments should make platform
investments in public assets and infrastructure to enable
shared value by business
• Government should regulate in a way
that reinforces and rewards shared value in business,
rather than working against it
26. Adding a Social Dimension to
Strategy
• Shared value opens up new
needs, new markets, and new value chain
configurations
• This creates new strategic
positions, and new opportunities for extending existing
positioning
?
• Companies should incorporate a
social dimension to their value proposition
• Shared value can reinforce
and even anchor a company"s strategy
• The social dimension of strategy can
be more sustainable vs. competitors than conventional cost
and quality advantages
27. Shared Value and Strategic
Positioning
Intrepid Travel
Value Proposition
• Sustainable small-group
travel
• Unique real-life experiences
involving significant interaction with the local
communities
• Cost-conscious, adventurous,
socially aware travelers looking for authentic
experiences
Mission
"Intrepid"s core purpose is to enrich
people"s lives by
creating unique, interactive travel
experiences. We provide
fun, affordable and sustainable travel that
is profitable for
Intrepid and beneficial to local
communities."
Distinctive Activities
• Smaller groups allows for frequent
use of local public transport, supporting local infrastructure
and reducing environmental impact
• Smaller groups allow stays at local
hotels and homestay opportunities as well as dining at local
restaurants
• Some trips involve community
volunteer projects where travellers help build local
infrastructure
• Significant training of local tour
guides and other local businesses such as hotels to improve
quality and efficiency
• Projects such as Kilimanjaro Porters
Assistance Project outfits 300+ porters per month with climbing
gear and has trained 10,000 porters in first aid, conversational
English, money management, and HIV/AIDS awareness since
2004
• Cooperation with Victoria University
to study the impact of small group travel on sensitive rural
communities
?
• Successful strategies in the future
will embody a significant shared value
dimension
28. The Purpose of
Business
• There is an opportunity to
transform thinking and practice about the role of the
corporation in society
• Shared value gives rise to far
broader approaches to economic value creation
• Shared value thinking will drive the
next wave of innovation, productivity enhancement,
and economic growth
• Businesses acting as
businesses, not as charitable givers, are arguably the most
powerful force for addressing many of the pressing issues facing
our society
• A transformation of business
practice around shared value will give purpose to the
corporation and represents our best chance to legitimize
business again
Autor:
Esteban de los
Ríos
 Página anterior Página anterior |   Volver al principio del trabajo Volver al principio del trabajo | Página siguiente  |